Ovarian Cysts Treatment
Find out more @ Harley Womens Health
How we treat ovarian cysts depends on their size, type, location, symptoms, and whether you have gone through menopause. Treatment options include watchful waiting, contraceptive pills, and surgery.

Ovarian Cysts Treatment Options
There are several ways to treat ovarian cysts, including:
- Watchful Waiting
- If the cyst is small and not causing any discomfort, your doctor may suggest “watchful waiting.” This means monitoring the cyst without immediate treatment.
- You may need an ultrasound every three months to check for any changes.
- Many cysts stay the same size, shrink, or even disappear on their own, so no action may be needed.
- This approach helps avoid unnecessary treatment.
- Contraceptive Pills
- For women with recurring ovarian cysts, oral contraceptive pills may be prescribed.
- These pills can stop ovulation and prevent new cysts from forming.
- Surgery
- Surgery may be needed if the cyst is large, persistent, painful, or appears cancerous.
- There are two types of surgery for removing ovarian cysts: laparoscopy and laparotomy.
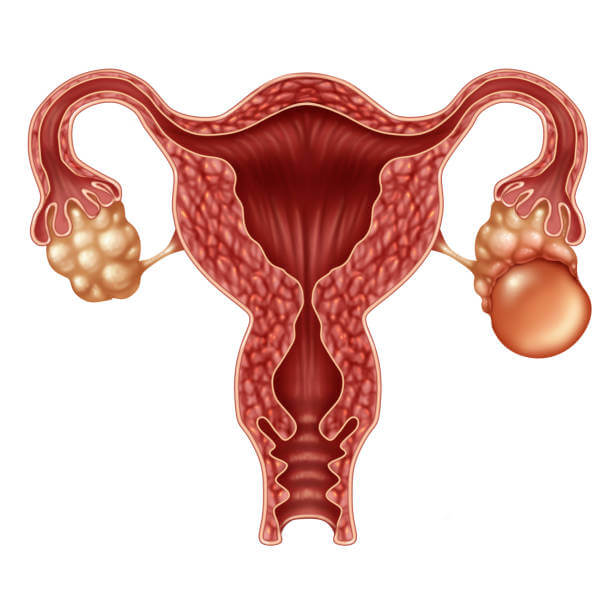
Types of Surgery
Laparoscopy (Keyhole Surgery)
- Most cysts can be removed with a minimally invasive procedure called laparoscopy.
- Small incisions (5-10mm) are made in the abdomen, and gas is used to inflate the pelvis.
- A camera and surgical instruments are inserted to remove the cyst while preserving healthy ovarian tissue.
- The cyst is then placed in a bag, decompressed, and removed without spilling any contents.
- This method involves quicker recovery times, shorter hospital stays, and a faster return to normal activities.
Laparotomy
- If the cyst is very large or potentially cancerous, a laparotomy may be necessary.
- A large incision is made in the abdomen to remove the cyst or ovary.
- The removed tissue is sent to a lab for cancer testing.
- This surgery is more invasive and typically requires a longer hospital stay.

Frequently Asked Questions
Do ovarian cysts always need to be removed?
- No, not all ovarian cysts need removal. Many functional cysts resolve on their own. Surgery is only needed if the cysts are persistent, symptomatic, or suspected to be cancerous.
Will I lose my ovary?
- Whether the ovary is removed depends on your age and the findings during surgery. If cancer is suspected, the ovary may need to be removed to prevent the cyst from rupturing.
How can I prevent recurrent ovarian cysts?
- Preventing ovarian cysts entirely may not be possible, but taking contraceptive pills can help reduce their formation.
What are the follow-up procedures after removal?
- If you don’t develop any symptoms after the cyst is removed, further tests aren’t usually needed. However, some cysts, like endometriomas and functional cysts, are more likely to return. If you’re concerned about recurrence, yearly pelvic ultrasounds are recommended.
